第5章 哈希表
第5章 哈希表
哈希表的设计
剑指offerⅡ30:插入、删除和随机访问都是O(1)的容器
剑指offerⅡ31:最近最少使用缓存
运用所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (Least Recently Used,最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
class LRUCache {
private DoublelyListNode head;
private DoublelyListNode tail;
private Map<Integer, DoublelyListNode> map;
private int capacity;
//这个DoublyListNode不能作为外部类,即使本地不报错,代码提交到leetcode平台时,只会提交LRUCache类,并不会提交外部类。
class DoublelyListNode {
public int key;
public int value;
public DoublelyListNode next;
public DoublelyListNode prev;
public DoublelyListNode(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
map = new HashMap<>();
head = new DoublelyListNode(-1, -1);//两个哨兵节点,便于插入删除
tail = new DoublelyListNode(-1, -1);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
DoublelyListNode node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
moveToTail(node, node.value);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
moveToTail(map.get(key), value);
} else {
DoublelyListNode node = new DoublelyListNode(key, value);
if (map.size() == capacity) {
DoublelyListNode toBeDeleted = head.next;
map.remove(toBeDeleted.key);
deleteNode(toBeDeleted);
}
insertToTail(node);
map.put(key, node);
}
}
//这个函数具有普遍意义。如果不修改node的value,就继续赋原值;否则赋新值。
private void moveToTail(DoublelyListNode node, int value) {
deleteNode(node);
node.value = value;
insertToTail(node);
}
private void deleteNode(DoublelyListNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void insertToTail(DoublelyListNode node) {
DoublelyListNode prev = tail.prev;
prev.next = node;
node.prev = prev;
node.next = tail;
tail.prev = node;
}
}
哈希表的应用
剑指offerⅡ32:有效的变位词
给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断它们是不是一组变位词(字母异位词)。
注意:若 *s* 和 *t* 中每个字符出现的次数都相同且字符顺序不完全相同,则称 *s* 和 *t* 互为变位词(字母异位词)。
示例 1:
输入: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
输出: true
示例 2:
输入: s = "rat", t = "car"
输出: false
示例 3:
输入: s = "a", t = "a"
输出: false
方法一:只考虑小写字母
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() != t.length() || s.equals(t)) {
return false;
}
int[] count = new int[26];
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
count[ch - 'a']++;
}
for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) {
if (--count[ch - 'a'] < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
方法二:不止小写字母
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if (s.length() != t.length() || s.equals(t)) {
return false;
}
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
map.put(ch, map.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
}
for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) {
map.put(ch, map.getOrDefault(ch, 0) - 1);
if (map.get(ch) < 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
剑指offerⅡ33:变位词组
给定一个字符串数组 strs ,将 变位词 组合在一起。 可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
**注意:**若两个字符串中每个字符出现的次数都相同,则称它们互为变位词。
示例 1:
输入: strs = ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"]
输出: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
方法一:排序
变位词排序后都是一样的,将排序后的String作为key,所有变位词的list当作value。
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ch);
String key = new String(ch);
List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<>());
list.add(str);
map.put(key, list);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
方法二:计数
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
int[] count = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
count[str.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
sb.append((char) (i + 'a'));
sb.append(count[i]);
}
String key = sb.toString();
List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<>());
list.add(str);
map.put(key, list);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
剑指offerⅡ34:外星语言是否排序
某种外星语也使用英文小写字母,但可能顺序 order 不同。字母表的顺序(order)是一些小写字母的排列。
给定一组用外星语书写的单词 words,以及其字母表的顺序 order,只有当给定的单词在这种外星语中按字典序排列时,返回 true;否则,返回 false。
示例 1:
输入:words = ["hello","leetcode"], order = "hlabcdefgijkmnopqrstuvwxyz"
输出:true
解释:在该语言的字母表中,'h' 位于 'l' 之前,所以单词序列是按字典序排列的。
示例 2:
输入:words = ["word","world","row"], order = "worldabcefghijkmnpqstuvxyz"
输出:false
解释:在该语言的字母表中,'d' 位于 'l' 之后,那么 words[0] > words[1],因此单词序列不是按字典序排列的。
示例 3:
输入:words = ["apple","app"], order = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
输出:false
解释:当前三个字符 "app" 匹配时,第二个字符串相对短一些,然后根据词典编纂规则 "apple" > "app",因为 'l' > '∅',其中 '∅' 是空白字符,定义为比任何其他字符都小(更多信息)。
方法:
class Solution {
public boolean isAlienSorted(String[] words, String order) {
int[] orderArray = new int[order.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < orderArray.length; i++) {
orderArray[order.charAt(i) - 'a'] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < words.length - 1; i++) {
if (!isOrder(words[i], words[i + 1], orderArray)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isOrder(String word1, String word2, int[] orderArray) {
int i = 0;
for (; i < word1.length() && i < word2.length(); i++) {
if (orderArray[word1.charAt(i) - 'a'] < orderArray[word2.charAt(i) - 'a']) {
return true;
} else if (orderArray[word1.charAt(i) - 'a'] > orderArray[word2.charAt(i) - 'a']) {
return false;
}
}
if (i == word1.length()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
剑指offerⅡ35:最小时间差
给定一个 24 小时制(小时:分钟HH:MM)的时间列表,找出列表中任意两个时间的最小时间差并以分钟数表示。
示例 1:
输入:timePoints = ["23:59","00:00"]
输出:1
示例 2:
输入:timePoints = ["00:00","23:59","00:00"]
输出:0
方法:
class Solution {
public int findMinDifference(List<String> timePoints) {
if (timePoints.size() > 1440) {
return 0;//鸽巢原理
}
boolean[] flags = new boolean[1440];
for (String timePoint : timePoints) {
String[] timePointSplitted = timePoint.split(":");
int time = Integer.parseInt(timePointSplitted[0]) * 60 + Integer.parseInt(timePointSplitted[1]);
if (flags[time] == true) {
return 0;
} else {
flags[time] = true;
}
}
return computeMin(flags);
}
private int computeMin(boolean[] flags) {
int start = 1440;
int end = -1;
int prev = -1;
int ans = 1440;
for (int i = 0; i < flags.length; i++) {
if (flags[i] == true) {
if (prev != -1) {
ans = Math.min(ans, i - prev);
}
prev = i;
start = Math.min(start, i);
end = Math.max(end, i);
}
}
return Math.min(ans, start + flags.length - end);
}
}
这道题的主要思路:将时间转换为分钟制,如果有重复直接返回时间差0。如果没有重复时间,用computeMin函数来计算最小时间差。这里有一个需要注意的地方:00:00-23:59时间差有1339,但是23:59-00:00只有1,所以需要用start记录最开始的有效时间时间,用end记录最末尾的有效时间,最后用答案和start + 1440 - end作比较,返回更小的值。
原地哈希
剑指offerⅠ03:数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为 n 的数组nums里的所有数字都在 [0, n-1] 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
示例 1:
输入:
[2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 5, 3]
输出:2 或 3
代码:
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (nums[i] != i) {
if (nums[i] == nums[nums[i]]) {
return nums[i];
}
swap(nums, i, nums[i]);
}
}
return -1;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
LC41:缺失的第一个正数
给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。
请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,0]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,4,-1,1]
输出:2
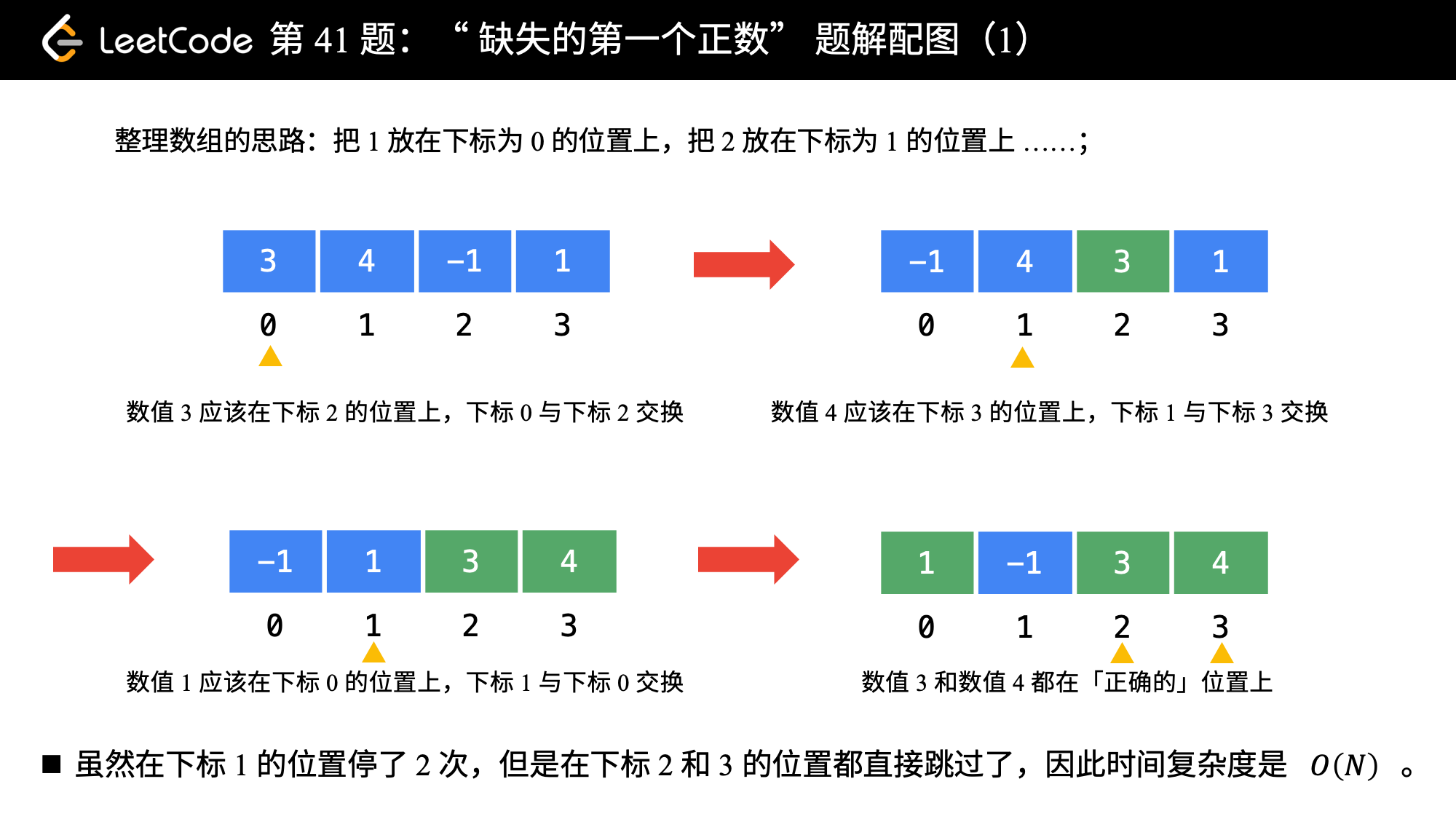
最早知道这个思路是在《剑指 Offer》这本书上看到的,感兴趣的朋友不妨做一下这道问题:剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字。下面简要叙述:
- 由于题目要求我们「只能使用常数级别的空间」,而要找的数一定在
[1, N + 1]左闭右闭(这里N是数组的长度)这个区间里。因此,我们可以就把原始的数组当做哈希表来使用。事实上,哈希表其实本身也是一个数组; - 我们要找的数就在
[1, N + 1]里,最后N + 1这个元素我们不用找。因为在前面的N个元素都找不到的情况下,我们才返回N + 1; - 那么,我们可以采取这样的思路:就把 1 这个数放到下标为 0 的位置, 2 这个数放到下标为 1 的位置,按照这种思路整理一遍数组。然后我们再遍历一次数组,第 1 个遇到的它的值不等于下标的那个数,就是我们要找的缺失的第一个正数。
- 这个思想就相当于我们自己编写哈希函数,这个哈希函数的规则特别简单,那就是数值为
i的数映射到下标为i - 1的位置。
我们来看一下这个算法是如何应用在示例 2 上的。
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (1 <= nums[i] && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1]) {
swap(nums, i, nums[i] - 1);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1) {
return i + 1;
}
}
return n + 1;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}