第15章 图
第15章 图
图的搜索
解题小经验:
- 如果面试题要求在无权图中找出两个节点之间的最短距离,那么广度优先搜索可能是更适合的算法。
- 如果面试题要求找出符合条件的所有路径,那么深度优先搜索可能是最合适的算法。
剑指offerⅡ105:最大的岛屿
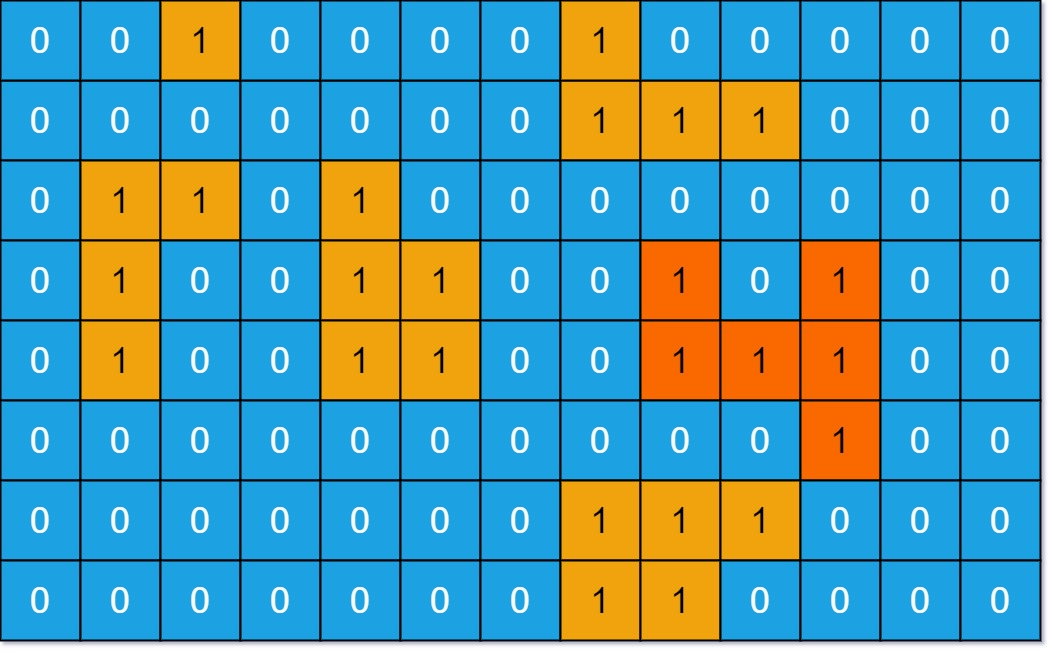
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的非空二维数组 grid ,用来表示海洋岛屿地图。
一个 岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在水平或者竖直方向上相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。
找到给定的二维数组中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。
示例 :
方法一:广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int maxArea = 0;
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[row][col];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, getArea(grid, visited, i, j));
}
}
}
return maxArea;
}
private int getArea(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int i, int j) {
Deque<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(new int[]{i, j});
visited[i][j] = true;
int area = 0;
int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] pos = q.pollFirst();
area++;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int r = pos[0] + dir[0];
int c = pos[1] + dir[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < grid.length && c >= 0 && c < grid[0].length && grid[r][c] == 1 && !visited[r][c]) {
q.offer(new int[]{r, c});
visited[r][c] = true;
}
}
}
return area;
}
}
方法二:深度优先搜索
将方法二代码第26行改成int[] pos = q.pollLast();即可。
方法三:基于递归的深度优先搜索
private int getArea(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int i, int j) {
int area = 1;
visited[i][j] = true;
int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int r = i + dir[0];
int c = j + dir[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < grid.length && c >= 0 && c < grid[0].length && grid[r][c] == 1 && !visited[r][c]) {
visited[r][c] = true;
area += getArea(grid, visited, r, c);
}
}
return area;
}
剑指offerⅡ106:二分图
存在一个 无向图 ,图中有 n 个节点。其中每个节点都有一个介于 0 到 n - 1 之间的唯一编号。
给定一个二维数组 graph ,表示图,其中 graph[u] 是一个节点数组,由节点 u 的邻接节点组成。形式上,对于 graph[u] 中的每个 v ,都存在一条位于节点 u 和节点 v 之间的无向边。该无向图同时具有以下属性:
- 不存在自环(
graph[u]不包含u)。 - 不存在平行边(
graph[u]不包含重复值)。 - 如果
v在graph[u]内,那么u也应该在graph[v]内(该图是无向图) - 这个图可能不是连通图,也就是说两个节点
u和v之间可能不存在一条连通彼此的路径。
二分图 定义:如果能将一个图的节点集合分割成两个独立的子集 A 和 B ,并使图中的每一条边的两个节点一个来自 A 集合,一个来自 B 集合,就将这个图称为 二分图 。
如果图是二分图,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
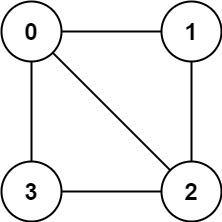
输入:graph = [[1,2,3],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,2]]
输出:false
解释:不能将节点分割成两个独立的子集,
示例 2:
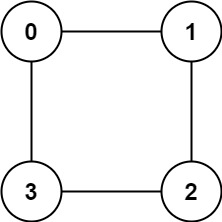
输入:graph = [[1,3],[0,2],[1,3],[0,2]]
输出:true
解释:可以将节点分成两组: {0, 2} 和 {1, 3} 。
分析:
将该图所有节点染成两种颜色,只要每一条边连接的两个节点异色,那么就是二分图。
colors[]为-1代表没有被着色,0和1分别代表两种颜色
方法一:BFS
class Solution {
public boolean isBipartite(int[][] graph) {
int[] colors = new int[graph.length];
Arrays.fill(colors, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
if (colors[i] == -1) {
//对每个连通子图进行BFS搜索
if (!setColor(graph, colors, i, 0)) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean setColor(int[][] graph, int[] colors, int i, int color) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(i);
colors[i] = color;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int v = queue.pollFirst();
//判断节点v的每个邻接节点
for (int neighbour : graph[v]) {
if (colors[neighbour] == -1) {
colors[neighbour] = 1 - colors[v];
queue.offer(neighbour);
} else {
if (colors[neighbour] == colors[v]) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
方法二:DFS
//递归地给i染色
private boolean setColor(int[][] graph, int[] colors, int i, int color) {
if (colors[i] != -1) {
return colors[i] == color;
}
colors[i] = color;
for (int neighbour : graph[i]) {
if (!setColor(graph, colors, neighbour, 1 - color)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
剑指offerⅡ107:矩阵中的距离
给定一个由 0 和 1 组成的矩阵 mat ,请输出一个大小相同的矩阵,其中每一个格子是 mat 中对应位置元素到最近的 0 的距离。
两个相邻元素间的距离为 1 。
示例 1:
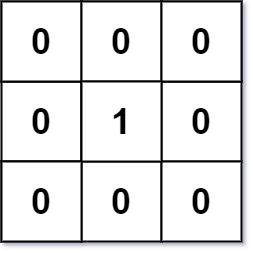
输入:mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
输出:[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
示例 2:
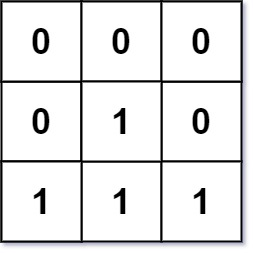
输入:mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
输出:[[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
算法:
class Solution {
public int[][] updateMatrix(int[][] mat) {
int row = mat.length;
int col = mat[0].length;
int[][] distances = new int[row][col];
Deque<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
distances[i][j] = 0;
} else {
distances[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
}
int[][] dirs = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] v = queue.pollFirst();
int distance = distances[v[0]][v[1]];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int r = v[0] + dir[0];
int c = v[1] + dir[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < row && c >= 0 && c < col) {
if(distances[r][c] > distance + 1){
distances[r][c] = distance + 1;
queue.offer(new int[]{r, c});
}
}
}
}
return distances;
}
}
剑指offerⅡ108:单词演变
在字典(单词列表) wordList 中,从单词 beginWord 和 endWord 的 转换序列 是一个按下述规格形成的序列:
- 序列中第一个单词是
beginWord。 - 序列中最后一个单词是
endWord。 - 每次转换只能改变一个字母。
- 转换过程中的中间单词必须是字典
wordList中的单词。
给定两个长度相同但内容不同的单词 beginWord 和 endWord 和一个字典 wordList ,找到从 beginWord 到 endWord 的 最短转换序列 中的 单词数目 。如果不存在这样的转换序列,返回 0。
**分析:**将每个单词看成是图中的一个节点,
单向BFS:
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
int length = 0;
Deque<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<String> notVisited = new HashSet<>(wordList);
queue.offer(beginWord);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
length++;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String word = queue.pollFirst();
if (word.equals(endWord)) {
return length;
}
List<String> neighbors = getNeighbors(word);
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
if (notVisited.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
notVisited.remove(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private List<String> getNeighbors(String word) {
List<String> neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char temp = chars[i];
for (char ch = 'a'; ch <= 'z'; ch++) {
if (temp != ch) {
chars[i] = ch;
neighbors.add(new String(chars));
}
}
chars[i] = temp;
}
return neighbors;
}
}
双向BFS:
下面的算法并没有用到队列,因为从一个set中得到是否包含一个元素,要比队列更快且更方便。
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> notVisited = new HashSet<>(wordList);
if (!notVisited.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
int length = 2;
Set<String> set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> set2 = new HashSet<>();
set1.add(beginWord);
set2.add(endWord);
while (!set1.isEmpty() && !set2.isEmpty()) {
if (set1.size() > set2.size()) {
Set<String> temp = set1;
set1 = set2;
set2 = temp;
}
Set<String> set3 = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : set1) {
List<String> neighbors = getNeighbors(word);
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
if (set2.contains(neighbor)) {
return length;
}
if (notVisited.contains(neighbor)) {
set3.add(neighbor);
notVisited.remove(neighbor);
}
}
}
length++;
set1 = set3;
}
return 0;
}
剑指offerⅡ109:开密码锁
一个密码锁由 4 个环形拨轮组成,每个拨轮都有 10 个数字: '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9' 。每个拨轮可以自由旋转:例如把 '9' 变为 '0','0' 变为 '9' 。每次旋转都只能旋转一个拨轮的一位数字。
锁的初始数字为 '0000' ,一个代表四个拨轮的数字的字符串。
列表 deadends 包含了一组死亡数字,一旦拨轮的数字和列表里的任何一个元素相同,这个锁将会被永久锁定,无法再被旋转。
字符串 target 代表可以解锁的数字,请给出解锁需要的最小旋转次数,如果无论如何不能解锁,返回 -1 。
示例 :
输入:deadends = ["0201","0101","0102","1212","2002"], target = "0202"
输出:6
解释:
可能的移动序列为 "0000" -> "1000" -> "1100" -> "1200" -> "1201" -> "1202" -> "0202"。
注意 "0000" -> "0001" -> "0002" -> "0102" -> "0202" 这样的序列是不能解锁的,因为当拨动到 "0102" 时这个锁就会被锁定。
**思路:**这个题和面试题108:单词演变很像,可以对比学习。但需要注意的是,该题统计的是跳转次数,面试题108:单词演变统计的是路径的单词数目。
单向BFS算法:
class Solution {
public int openLock(String[] deadends, String target) {
Set<String> dead = new HashSet<>();
for (String deadend : deadends) {
dead.add(deadend);
}
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
if (dead.contains("0000") || dead.contains(target)) {
return -1;
}
Deque<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int ans = 0;
queue.offer("0000");
visited.add("0000");
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String number = queue.pollFirst();
if (number.equals(target)) {
return ans;
}
List<String> neighbors = findNeighbors(number);
for (String neighbor : neighbors) {
if (!visited.contains(neighbor) && !dead.contains(neighbor)) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
visited.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
ans++;
}
return -1;
}
private List<String> findNeighbors(String number) {
List<String> neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
char[] chars = number.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char old = chars[i];
chars[i] = old == '9' ? '0' : (char) (old + 1);
neighbors.add(new String(chars));
chars[i] = old == '0' ? '9' : (char) (old - 1);
neighbors.add(new String(chars));
chars[i] = old;
}
return neighbors;
}
}
双向BFS算法:
剑指offerⅡ110:所有路径
给定一个有 n 个节点的有向无环图,用二维数组 graph 表示,请找到所有从 0 到 n-1 的路径并输出(不要求按顺序)。
graph 的第 i 个数组中的单元都表示有向图中 i 号节点所能到达的下一些结点(译者注:有向图是有方向的,即规定了 a→b 你就不能从 b→a ),若为空,就是没有下一个节点了。
示例 :
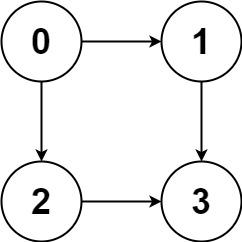
输入:graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]
输出:[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
解释:有两条路径 0 -> 1 -> 3 和 0 -> 2 -> 3
思路:和[回溯法专题](../#第13章 回溯法)对比学习,回溯法本质上就是DFS。
算法:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
dfs(0, ans, path, graph);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int i, List<List<Integer>> ans, LinkedList<Integer> path, int[][] graph) {
path.add(i);
if (i == graph.length - 1) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int next : graph[i]) {
dfs(next, ans, path, graph);
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
剑指offerⅡ111:计算除法
给定一个变量对数组 equations 和一个实数值数组 values 作为已知条件,其中 equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] 和 values[i] 共同表示等式 Ai / Bi = values[i] 。每个 Ai 或 Bi 是一个表示单个变量的字符串。
另有一些以数组 queries 表示的问题,其中 queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] 表示第 j 个问题,请你根据已知条件找出 Cj / Dj = ? 的结果作为答案。
返回 所有问题的答案 。如果存在某个无法确定的答案,则用 -1.0 替代这个答案。如果问题中出现了给定的已知条件中没有出现的字符串,也需要用 -1.0 替代这个答案。
**注意:**输入总是有效的。可以假设除法运算中不会出现除数为 0 的情况,且不存在任何矛盾的结果。
示例 1:
输入:equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [["a","c"],["b","a"],["a","e"],["a","a"],["x","x"]]
输出:[6.00000,0.50000,-1.00000,1.00000,-1.00000]
解释:
条件:a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0
问题:a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ?
结果:[6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ]
示例 2:
输入:equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"],["bc","cd"]], values = [1.5,2.5,5.0], queries = [["a","c"],["c","b"],["bc","cd"],["cd","bc"]]
输出:[3.75000,0.40000,5.00000,0.20000]
示例 3:
输入:equations = [["a","b"]], values = [0.5], queries = [["a","b"],["b","a"],["a","c"],["x","y"]]
输出:[0.50000,2.00000,-1.00000,-1.00000]
代码:
剑指offerⅡ112:最长递增路径
给定一个 m x n 整数矩阵 matrix ,找出其中 最长递增路径 的长度。
对于每个单元格,你可以往上,下,左,右四个方向移动。 不能 在 对角线 方向上移动或移动到 边界外(即不允许环绕)。
示例 1:
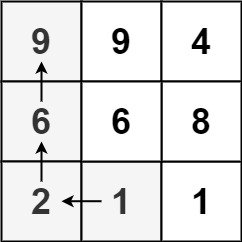
输入:matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
输出:4
解释:最长递增路径为 [1, 2, 6, 9]
class Solution {
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
if(row == 0 || col == 0){
return 0;
}
int[][] lengths = new int[row][col];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
int length = dfs(i, j, matrix, lengths);
ans = Math.max(length, ans);
}
}
return ans;
}
private int dfs(int i, int j, int[][] matrix, int[][] lengths) {
if (lengths[i][j] != 0) {
return lengths[i][j];
}
int length = 1;
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int[][] dirs = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int r = i + dir[0];
int c = j + dir[1];
if (r >= 0 && r < row && c >= 0 && c < col && matrix[r][c] > matrix[i][j]) {
int path = dfs(r, c, matrix, lengths);
length = Math.max(path + 1, length);
}
}
lengths[i][j] = length;
return length;
}
}
LC79:矩阵中的路径
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
例如,在下面的 3×4 的矩阵中包含单词 "ABCCED"(单词中的字母已标出)。
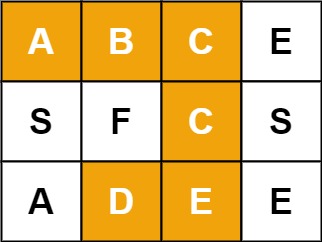
示例 1:
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], word = "abcd"
输出:false
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
int m = board.length;
int n = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (dfs(board, words, i, j, 0)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean dfs(char[][] board, char[] words, int i, int j, int k) {
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.length || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] != words[k]) {
return false;
}
if (k == words.length - 1) {
return true;
}
board[i][j] = '1';
boolean ans = dfs(board, words, i + 1, j, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, words, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, words, i, j + 1, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, words, i, j - 1, k + 1);
board[i][j] = words[k];
return ans;
}
}
剑指offerⅠ13:机器人的运动范围
地上有一个m行n列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 到坐标 [m-1,n-1] 。一个机器人从坐标 [0, 0] 的格子开始移动,它每次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格(不能移动到方格外),也不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格 [35, 37] ,因为3+5+3+7=18。但它不能进入方格 [35, 38],因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
示例 1:
输入:m = 2, n = 3, k = 1
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:m = 3, n = 1, k = 0
输出:1
代码:
class Solution {
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
Deque<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean visited[][] = new boolean[m][n];
queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0});
visited[0][0] = true;
int ans = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] node = queue.pollFirst();
ans++;
int[][] dirs = {{0 ,1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}};
for(int[] dir : dirs){
int r = node[0] + dir[0];
int c = node[1] + dir[1];
if(check(r, c, m, n, k, visited)){
queue.offer(new int[]{r, c});
visited[r][c] = true;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
private boolean check(int i, int j, int m, int n, int k, boolean[][] visited){
if(i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n && getSum(i) + getSum(j) <= k && visited[i][j] == false)
return true;
return false;
}
private int getSum(int num){
int sum = 0;
while(num > 0){
sum = sum + num % 10;
num = num / 10;
}
return sum;
}
}
剑指offerⅠ14:课程顺序
地上有一个m行n列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 到坐标 [m-1,n-1] 。一个机器人从坐标 [0, 0] 的格子开始移动,它每次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格(不能移动到方格外),也不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格 [35, 37] ,因为3+5+3+7=18。但它不能进入方格 [35, 38],因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
示例 1:
输入:m = 2, n = 3, k = 1
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:m = 3, n = 1, k = 0
输出:1
拓扑排序
剑指offerⅡ113:课程顺序
现在总共有 numCourses 门课需要选,记为 0 到 numCourses-1。
给定一个数组 prerequisites ,它的每一个元素 prerequisites[i] 表示两门课程之间的先修顺序。 例如 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] 表示想要学习课程 ai ,需要先完成课程 bi 。
请根据给出的总课程数 numCourses 和表示先修顺序的 prerequisites 得出一个可行的修课序列。
可能会有多个正确的顺序,只要任意返回一种就可以了。如果不可能完成所有课程,返回一个空数组。
示例 1:
输入: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]]
输出: [0,1]
解释: 总共有 2 门课程。要学习课程 1,你需要先完成课程 0。因此,正确的课程顺序为 [0,1] 。
示例 2:
输入: numCourses = 4, prerequisites = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]]
输出: [0,1,2,3] or [0,2,1,3]
解释: 总共有 4 门课程。要学习课程 3,你应该先完成课程 1 和课程 2。并且课程 1 和课程 2 都应该排在课程 0 之后。
因此,一个正确的课程顺序是 [0,1,2,3] 。另一个正确的排序是 [0,2,1,3] 。
示例 3:
输入: numCourses = 1, prerequisites = []
输出: [0]
解释: 总共 1 门课,直接修第一门课就可。
代码:
class Solution {
public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
graph.put(i, new LinkedList<>());
}
int[] inDegrees = new int[numCourses];
for (int[] prerequisite : prerequisites) {
graph.get(prerequisite[1]).add(prerequisite[0]);
inDegrees[prerequisite[0]]++;
}
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++) {
if (inDegrees[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i);
}
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.pollFirst();
ans.add(node);
for (int next : graph.get(node)) {
inDegrees[next]--;
if (inDegrees[next] == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
return ans.size() == numCourses
? ans.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray()
: new int[0];
}
}
剑指offerⅡ114:外星文字典
现有一种使用英语字母的外星文语言,这门语言的字母顺序与英语顺序不同。
给定一个字符串列表 words ,作为这门语言的词典,words 中的字符串已经 按这门新语言的字母顺序进行了排序 。
请你根据该词典还原出此语言中已知的字母顺序,并 按字母递增顺序 排列。若不存在合法字母顺序,返回 "" 。若存在多种可能的合法字母顺序,返回其中 任意一种 顺序即可。
字符串 s 字典顺序小于 字符串 t 有两种情况:
- 在第一个不同字母处,如果
s中的字母在这门外星语言的字母顺序中位于t中字母之前,那么s的字典顺序小于t。 - 如果前面
min(s.length, t.length)字母都相同,那么s.length < t.length时,s的字典顺序也小于t。
示例 1:
输入:words = ["wrt","wrf","er","ett","rftt"]
输出:"wertf"
示例 2:
输入:words = ["z","x"]
输出:"zx"
示例 3:
输入:words = ["z","x","z"]
输出:""
解释:不存在合法字母顺序,因此返回 "" 。
代码:
class Solution {
public String alienOrder(String[] words) {
Map<Character, Set<Character>> graph = new HashMap<>();
Map<Character, Integer> inDegrees = new HashMap<>();
for (String word : words) {
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
graph.put(ch, new HashSet<>());
inDegrees.put(ch, 0);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < words.length; i++) {
String word1 = words[i - 1];
String word2 = words[i];
if (word1.startsWith(word2) && !word1.equals(word2)) {
return "";
}
for (int j = 0; j < word1.length() && j < word2.length(); j++) {
char ch1 = word1.charAt(j);
char ch2 = word2.charAt(j);
if (ch1 != ch2) {
if (!graph.get(ch1).contains(ch2)) {
graph.get(ch1).add(ch2);
inDegrees.put(ch2, inDegrees.get(ch2) + 1);
}
break;
}
}
}
Deque<Character> queue = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (char ch : graph.keySet()) {
if (inDegrees.get(ch) == 0) {
queue.offer(ch);
}
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
char character = queue.pollFirst();
sb.append(character);
for (char next : graph.get(character)) {
inDegrees.put(next, inDegrees.get(next) - 1);
if (inDegrees.get(next) == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
return sb.length() == inDegrees.size() ? sb.toString() : "";
}
}
剑指offerⅡ115:重建序列
请判断原始的序列 org 是否可以从序列集 seqs 中唯一地 重建 。
序列 org 是 1 到 n 整数的排列,其中 1 ≤ n ≤ 104。重建 是指在序列集 seqs 中构建最短的公共超序列,即 seqs 中的任意序列都是该最短序列的子序列。
示例 1:
输入: org = [1,2,3], seqs = [[1,2],[1,3]]
输出: false
解释:[1,2,3] 不是可以被重建的唯一的序列,因为 [1,3,2] 也是一个合法的序列。
示例 2:
输入: org = [1,2,3], seqs = [[1,2]]
输出: false
解释:可以重建的序列只有 [1,2]。
示例 3:
输入: org = [1,2,3], seqs = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
输出: true
解释:序列 [1,2], [1,3] 和 [2,3] 可以被唯一地重建为原始的序列 [1,2,3]。
示例 4:
输入: org = [4,1,5,2,6,3], seqs = [[5,2,6,3],[4,1,5,2]]
输出: true
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean sequenceReconstruction(int[] org, List<List<Integer>> seqs) {
if (seqs.size() == 0) {
return false;
}
int n = org.length;
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
graph.put(i, new HashSet<>());
}
int[] inDegrees = new int[n];//inDegrees[i] 对应i + 1的入度
for (List<Integer> seq : seqs) {
for (int num : seq) {
if (num < 1 || num > n) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < seq.size(); i++) {
int first = seq.get(i - 1);
int second = seq.get(i);
if (!graph.get(first).contains(second)) {
graph.get(first).add(second);
inDegrees[second - 1]++;
}
}
}
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (inDegrees[i] == 0) {
queue.offer(i + 1);
}
}
int length = 0;
int[] ans = new int[n];
while (queue.size() == 1) {
int first = queue.pollFirst();
ans[length++] = first;
for (int next : graph.get(first)) {
inDegrees[next - 1]--;
if (inDegrees[next - 1] == 0) {
queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
return Arrays.equals(org, ans);
}
}
并查集
并查集是一种树型数据结构,用于处理一些不交集的合并及查询问题。
Find:确定元素属于哪一个自己。它可以被用来确定两个元素是否属于同一个子集;
Union:将两个自己合并成同一个集合。
生活中的例子:
- 小弟->老大
- 帮派识别
- 两种优化方式
优化方法一:union的时候,将更深度次深的树的root指向更深的树的root;
优化方法二:这个更常用。每个Union的各个节点只指向root。
剑指offerⅡ116:省份数量
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
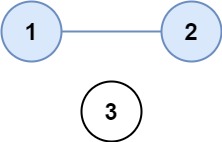
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:2
示例 2:
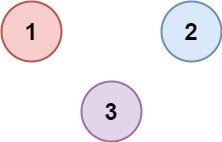
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:3
方法一:广度优先搜索
class Solution {
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.length;
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[n];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
bfs(isConnected, isVisited, i);
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
private void bfs(int[][] isConnected, boolean[] isVisited, int city) {
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(city);
isVisited[city] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int thisCity = queue.pollFirst();
for (int i = 0; i < isConnected.length; i++) {
if (isConnected[thisCity][i] == 1 && !isVisited[i]) {
queue.offer(i);
isVisited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
方法二:深度优先搜索
class Solution {
public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.length;
boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[n];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isConnected, isVisited, i);
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int[][] isConnected, boolean[] isVisited, int city) {
isVisited[city] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < isConnected.length; i++) {
if (isConnected[city][i] == 1 && !isVisited[i]) {
dfs(isConnected, isVisited, i);
}
}
}
}
方法三:并查集
剑指offerⅡ写法:
极客时间写法:
剑指offerⅡ117:相似的字符串
LC 839
如果交换字符串 X 中的两个不同位置的字母,使得它和字符串 Y 相等,那么称 X 和 Y 两个字符串相似。如果这两个字符串本身是相等的,那它们也是相似的。
例如,"tars" 和 "rats" 是相似的 (交换 0 与 2 的位置); "rats" 和 "arts" 也是相似的,但是 "star" 不与 "tars","rats",或 "arts" 相似。
总之,它们通过相似性形成了两个关联组:{"tars", "rats", "arts"} 和 {"star"}。注意,"tars" 和 "arts" 是在同一组中,即使它们并不相似。形式上,对每个组而言,要确定一个单词在组中,只需要这个词和该组中至少一个单词相似。
给定一个字符串列表 strs。列表中的每个字符串都是 strs 中其它所有字符串的一个 字母异位词 。请问 strs 中有多少个相似字符串组?
字母异位词(anagram),一种把某个字符串的字母的位置(顺序)加以改换所形成的新词。
示例 1:
输入:strs = ["tars","rats","arts","star"]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:strs = ["omv","ovm"]
输出:1
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 3001 <= strs[i].length <= 300strs[i]只包含小写字母。strs中的所有单词都具有相同的长度,且是彼此的字母异位词。
剑指offerⅡ118:多余的边
LC 684
树可以看成是一个连通且 无环 的 无向 图。
给定往一棵 n 个节点 (节点值 1~n) 的树中添加一条边后的图。添加的边的两个顶点包含在 1 到 n 中间,且这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。图的信息记录于长度为 n 的二维数组 edges ,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
请找出一条可以删去的边,删除后可使得剩余部分是一个有着 n 个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回数组 edges 中最后出现的边。
示例 1:
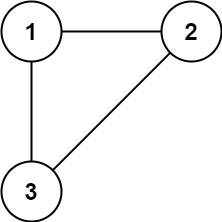
输入: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
输出: [2,3]
示例 2:
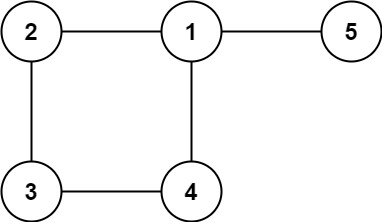
输入: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]]
输出: [1,4]
提示:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != biedges中无重复元素- 给定的图是连通的
剑指offerⅡ119:最长连续序列
LC 128
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
输出:4
解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1]
输出:9
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
**进阶:**可以设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的解决方案吗?